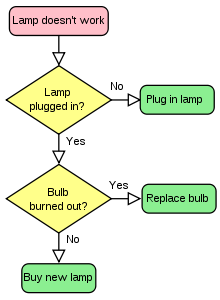
In mathematics, computer science, and related subjects, an algorithm (derived from the name of mathematician al-Khwārizmī)
is an effective method for solving a problem expressed as a finite sequence of steps. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and many other fields. (In more advanced or abstract settings, the instructions do not necessarily constitute a finite sequence, and even not necessarily a sequence; see, e.g., "nondeterministic algorithm".)
Each algorithm is a list of well-defined instructions for completing a task. Starting from an initial state, the instructions describe a computation that proceeds through a well-defined series of successive states, eventually terminating in a final ending state. The transition from one state to the next is not necessarily deterministic; some algorithms, known as randomized algorithms, incorporate randomness.


